What are the main ESG frameworks?
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) frameworks are used by companies and investors to evaluate and report on their performance in these areas. Some of the main ESG framework include:
- Global Reporting Initiative (GRI): This is a widely-used framework for sustainability reporting, which provides guidelines and indicators for companies to report on their environmental, social, and governance performance.
- Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB): This framework identifies the ESG factors most relevant to specific industries and provides a standardized set of sustainability accounting standards for companies to report on.
- Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD): This framework provides recommendations for companies to disclose their climate-related risks and opportunities, in order to help investors make more informed decisions.
- Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP): This framework enables companies and cities to disclose their environmental impact and climate risk, and provides a platform for investors to access this information.
- United Nations Global Compact (UNGC): This is a voluntary initiative for companies to commit to ten principles in the areas of human rights, labor, environment, and anti-corruption.
- Principles for Responsible Investment (PRI): This is a global initiative for investors to incorporate ESG factors into their investment decisions and ownership practices.
- Dow Jones Sustainability Indices (DJSI): This framework evaluates the ESG and sustainability performance of companies based on a range of ESG factors, and provides a benchmark for investors to track their progress.
These are some of the main ESG frameworks, but there are many others that companies and investors may use depending on their specific needs and objectives.
What are the 3 pillars of ESG?
The 3 pillars of ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) are as follows:
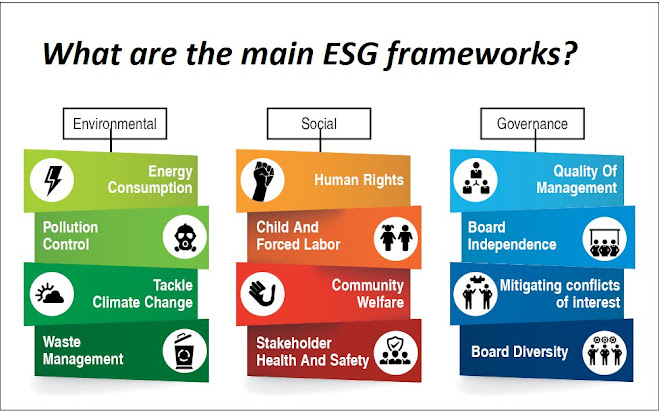
- Environmental: This pillar focuses on a company's impact on the natural environment, including factors such as carbon emissions, waste management, energy efficiency, water usage, and biodiversity. Environmental factors are becoming increasingly important as climate change and other environmental issues gain greater attention from investors, regulators, and the public.
- Social: This pillar considers a company's impact on its stakeholders, including employees, customers, suppliers, communities, and society at large. Social factors can include issues such as labor practices, human rights, diversity and inclusion, product safety, customer privacy, and community engagement.
- Governance: This pillar focuses on a company's leadership, management structures, and policies, and includes factors such as board composition, executive compensation, risk management, shareholder rights, and transparency. Good governance is seen as critical to ensuring that a company operates in a responsible and sustainable manner, and is accountable to its stakeholders.
What is the ESG framework in India?
In India, there are several ESG frameworks that companies and investors may use to evaluate and report on their environmental, social, and governance performance. Some of the key frameworks include:
- Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) Listing Regulations: These regulations require companies listed on Indian stock exchanges to disclose information related to their ESG performance, including policies, initiatives, and risks. The regulations also require companies to have a board-level ESG committee and to include ESG considerations in their annual reports.
- National Voluntary Guidelines on Social, Environmental and Economic Responsibilities of Business (NVGs): These guidelines, developed by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, provide a framework for companies to integrate ESG considerations into their business practices. The NVGs cover a range of topics, including governance, human rights, environment, and stakeholder engagement.
- Indian Green Building Council (IGBC) Green Business Certification: This certification recognizes companies that demonstrate leadership in environmental sustainability report, including energy efficiency, water conservation, and waste management. The certification is based on a set of criteria developed by the IGBC, which is a part of the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII).
- BSE SAM Sustainability Index: This index, developed by the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and SAM Sustainable Asset Management, tracks the performance of companies in India that demonstrate strong ESG performance. The index is based on a set of criteria developed by SAM, which includes factors such as environmental management, social practices, and governance.
These are some of the main ESG frameworks in India, but there are also many other initiatives and standards that companies and investors may use to evaluate and report on their ESG performance.
How to build an ESG framework?
Building an Environmental, Social, and ESG corporate governance involves a structured approach that integrates ESG considerations into the decision-making processes of an organization. Here are the steps to building an ESG framework:
- Identify the organization's ESG priorities: Determine the most critical ESG factors that are relevant to the organization's industry, operations, and stakeholders.
- Define the ESG framework's scope and objectives: Define the ESG framework's purpose, including the areas of focus, target audience, and desired outcomes.
- Develop a governance structure: Establish a governance structure that assigns responsibilities for implementing and monitoring the ESG framework, including a clear definition of the roles and responsibilities of senior management, employees, and other stakeholders.
- Establish metrics and targets: Define the key performance indicators (KPIs) that will be used to monitor and measure the organization's progress towards achieving its ESG objectives. The KPIs should be aligned with the organization's strategic goals and be consistent with recognized industry standards and best practices.
- Embed ESG considerations into business processes: Ensure that ESG considerations are integrated into the organization's decision-making processes, such as strategic planning, risk management, procurement, and supply chain management.
- Implement monitoring and reporting mechanisms: Develop a system to monitor and report on ESG performance, including periodic reporting to senior management and the board of directors, as well as regular communication with stakeholders.
- Continuously improve the ESG framework: Regularly review and update the ESG framework to ensure that it remains relevant and effective, reflecting changes in the organization's operations, stakeholder expectations, and emerging industry trends.
Overall, building an ESG framework requires a collaborative effort between various stakeholders within the organization, including senior management, employees, and external partners, to embed ESG considerations into the organization's decision-making processes and operations.
What framework is used for ESG reporting?
There are several frameworks used for ESG reporting, each with its own unique features and benefits. Here are some of the most widely used frameworks for ESG reporting:
- Global Reporting Initiative (GRI): The GRI Standards is one of the most widely used ESG reporting frameworks. It provides a comprehensive set of indicators that cover a wide range of ESG issues, including governance, social, and environmental impacts.
- Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB): The SASB Standards are industry-specific and provide a set of disclosure standards for financially material ESG issues. This framework is focused on financial materiality and aims to help investors make informed investment decisions based on ESG factors.
- Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD): The TCFD framework provides recommendations for companies to disclose climate-related ESG financial risks and opportunities. It aims to help companies provide more transparent and useful information to investors, lenders, and other stakeholders.
- Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP): The CDP is an organization that works with companies and investors to disclose environmental impacts, including carbon emissions, climate risks, and water management. The CDP provides a global platform for companies to report on their environmental performance and receive feedback from stakeholders.
- Integrated Reporting (IR): The IR framework is a principles-based approach to reporting that aims to provide a holistic view of the organization's value creation process, including its financial, social, and environmental impacts. The IR framework aims to help companies communicate a clear and concise message to stakeholders about their overall performance and value creation.
Overall, the choice of ESG reporting framework will depend on the organization's industry, stakeholder expectations, and reporting objectives. Many organizations use a combination of these frameworks to provide a comprehensive and meaningful ESG report.
Read more This Blog :- ESG Investing: A Guide for Small Investors


Comments
Post a Comment