What Is Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG)
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) is a framework used to evaluate the sustainability and societal impact of a company or organization. It is a comprehensive evaluation of a company's overall sustainability and impact on the environment, society, and governance.
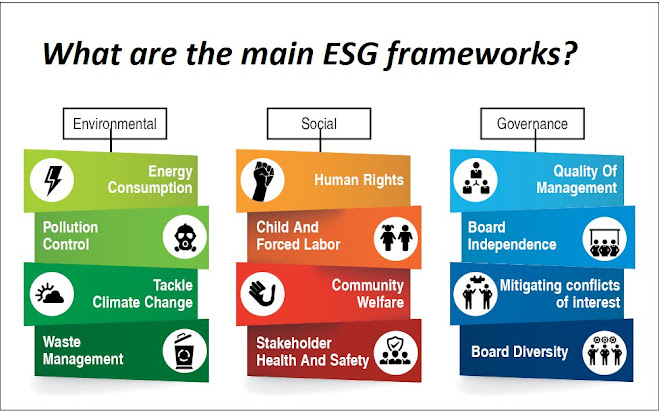
Environmental factors include a company's impact on the natural environment, such as its carbon emissions, energy consumption, and water usage. Social factors include a company's impact on society, such as its labor practices, human rights record, and community engagement. Governance factors include a company's internal governance structure, such as its board composition, executive compensation, and transparency.
ESG analysis is used by investors, companies, and other stakeholders to evaluate the overall sustainability of a company and to identify potential risks and opportunities. It can also be used to identify companies that are leading the way in sustainable practices and to identify areas where companies need to improve.
ESG data is used increasingly by investors and asset managers to make investment decisions, as well as by other stakeholders, such as customers and employees, to evaluate a company's overall performance. It is also used by rating agencies to assign sustainability ratings to companies, which can affect the company's ability to raise capital and its reputation among stakeholders.
ESG framework factors are becoming increasingly important for companies and organizations as global concerns about climate change, social inequality, and corporate governance have risen. It is becoming an important consideration for many investors and stakeholders, as it helps them to assess a company's long-term financial performance and stability.
- Understand your stakeholders: Identify the key stakeholders in your business, including customers, employees, investors, and suppliers, and understand their priorities and concerns.
- Assess your current performance: Evaluate your current environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance using internal and external data sources.
- Set specific, measurable goals: Develop specific, measurable ESG goals that align with your business objectives and address the concerns of your stakeholders.
- Implement a plan: Develop a plan to achieve your ESG goals, including clear milestones and metrics for tracking progress.
- Communicate and report: Communicate your ESG sustainability goals and progress to stakeholders, and report on your performance using industry-standard frameworks such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) or the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB).
How do you create an ESG goal?
Creating an ESG goal involves the following steps:
- Define the area of focus: Identify the specific area of environmental, social, or governance concern that you want to address, such as reducing carbon emissions, improving employee diversity and inclusion, or enhancing corporate transparency.
- Determine the scope of the goal: Decide on the scope of the goal, such as the time frame, geographic location, and specific operations or products that will be covered.
- Set a measurable target: Establish a specific and measurable target for the goal, such as reducing carbon emissions by a certain percentage or increasing the representation of underrepresented groups in leadership positions.
- Develop an action plan: Create an action plan outlining the steps that will be taken to achieve the goal, including timelines, responsibilities, and resources required.
- Monitor and report progress: Regularly monitor progress towards achieving the goal, and report on progress and any challenges encountered to stakeholders, such as employees, customers, and investors.
- Review and adjust as needed: Regularly review the goal and make adjustments as needed to ensure that it remains aligned with the company's overall strategy and goals, and addresses the concerns of stakeholders.
How to Develop an ESG Strategy
Developing an environmental, social, and governance (ESG) strategy involves several key steps:
- Understand the business: Understand the key drivers of your business and assess the environmental, social, and governance risks and opportunities that are most relevant to your operations and stakeholders.
- Define ESG objectives: Define clear and measurable ESG objectives that align with your overall business strategy and address the concerns of your stakeholders.
- Conduct a materiality assessment: Conduct a materiality assessment to identify the most critical environment ESG issues for your business, and prioritize them based on their potential impact on your operations, reputation, and stakeholders.
- Develop an action plan: Develop an action plan outlining the specific steps that will be taken to achieve your ESG objectives, including timelines, responsibilities, and resources required.
- Implement and monitor: Implement the action plan, and regularly monitor and report on progress towards achieving the ESG objectives, using industry-standard frameworks such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) or the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB).
- Communicate and engage: Communicate your ESG strategy and progress to stakeholders, and engage with them to understand their concerns and gather feedback.
- Continuously review: Continuously review and update the strategy, taking into account new developments, changing regulations, and evolving stakeholder expectations.
A framework for developing your ESG strategy
A framework for developing an environmental, social, and governance (ESG) strategy can include the following steps:
- Define the scope: Define the scope of the ESG strategy, including the geographic location, business units, and products or services that will be covered.
- Conduct a materiality assessment: Identify the most critical ESG issues for your business and its stakeholders, such as climate change, human rights, or corporate governance.
- Identify risks and opportunities: Assess the risks and opportunities associated with the identified ESG issues, including their potential impact on your operations, reputation, and stakeholders.
- Set goals and targets: Set clear, measurable, and time-bound ESG goals and targets that align with your overall business strategy.
- Develop an action plan: Develop an action plan outlining the specific steps that will be taken to achieve your ESG goals, including timelines, responsibilities, and resources required.
- Implement and monitor: Implement the action plan, and regularly monitor and report on progress towards achieving the ESG goals.
- Communicate and engage: Communicate your ESG strategy and progress to stakeholders, and engage with them to understand their concerns and gather feedback.
- Continuously review and improve: Continuously review and improve your ESG strategy, taking into account new developments, changing regulations, and evolving stakeholder expectations.
- Integrate ESG into decision making: Integrate ESG considerations into all aspects of your business decision making process.
- Assign accountability: Assign accountability for ESG consulting performance to specific individuals or teams within the organization.
Conclusion
ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance. It is a framework used to evaluate the sustainability and societal impact of a company or organization.
Environmental factors include a company's impact on the natural environment, such as its carbon emissions, energy consumption, and water usage.
Social factors include a company's impact on society, such as its labor practices, human rights record, and community engagement.
Governance factors include a company's internal governance structure, such as its board composition, executive compensation, and transparency.
The summary of ESG environmental social is that it is a comprehensive evaluation of a company's overall sustainability and impact on the environment, society, and governance, which can help investors, customers, and other stakeholders to evaluate the company's performance and potential risks.
Original Source
.jpg)


Comments
Post a Comment