What is ESG? An Environmental, Social and Governance Guide
ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance. It is a set of criteria used to evaluate a company's performance and impact on the environment, society, and the company's internal governance structure. ESG environmental factors are becoming inc66reasingly important to investors, as they provide a comprehensive understanding of a company's operations and risk profile.
Here is a brief overview of each of the ESG components:
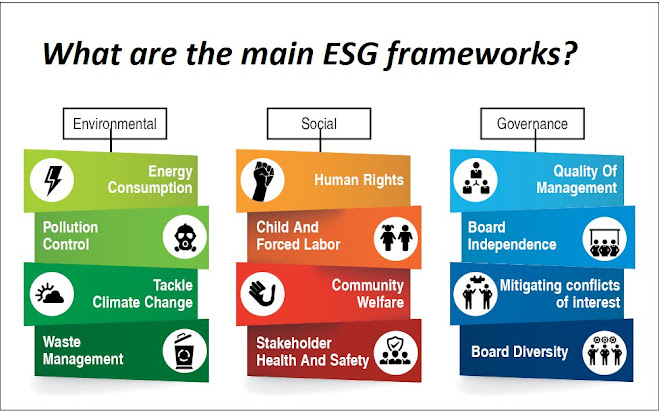
- Environmental: This refers to a company's impact on the natural environment, such as its carbon footprint, energy consumption, waste management practices, and water usage.
- Social: This refers to a company's impact on society, including its relationships with employees, customers, suppliers, and the communities where it operates. It also includes factors such as diversity, equity, and inclusion, human rights, labor practices, and product safety.
- Governance: This refers to a company's internal governance structure, including its board of directors, executive compensation, shareholder rights, and transparency in financial reporting.
By considering these ESG factors, investors and other stakeholders can evaluate a company's long-term sustainability and ethical practices. This can help inform investment decisions and influence corporate behavior.
What is ESG investing?
ESG investing, also known as sustainable investing, is an investment approach that takes into account the Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors of a company when making investment decisions. The goal of ESG investing is to invest in companies that demonstrate sustainable and responsible business practices, while avoiding those that have a negative impact on the environment, society, or governance.
ESG investing involves a range of different strategies, including:
- Negative screening: This approach involves excluding companies or industries that are considered to have a negative impact on the environment or society, such as fossil fuel companies or tobacco producers.
- Positive screening: This approach involves selecting companies that have a positive impact on the environment or society, such as those involved in renewable energy or social justice initiatives.
- ESG integration: This approach involves incorporating ESG factors into traditional financial analysis to identify companies with strong ESG performance and long-term sustainability.
- Impact investing: This approach involves investing in companies or funds that have a specific social or environmental goal, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions or promoting gender diversity.
ESG investing has become increasingly popular in recent years, as more investors seek to align their investments with their values and contribute to a more sustainable and responsible economy.
What is ESG reporting?
ESG reporting refers to the process of disclosing a company's Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) performance and impact to stakeholders, including investors, customers, employees, and the public. ESG reporting can take many forms, including annual reports, sustainability reports, and disclosures to regulatory bodies.
ESG reporting typically includes a range of information related to a company's ESG practices and performance, including:
- Environmental performance: This includes data on a company's greenhouse gas emissions, water and energy use, waste management practices, and other environmental impacts.
- Social performance: This includes data on a company's employee practices, such as diversity and inclusion, employee health and safety, and labor standards. It may also include information on a company's impact on communities, such as philanthropic activities, local sourcing, or community engagement.
- Governance performance: This includes data on a company's board structure, executive compensation, and other governance practices that impact long-term sustainability.
ESG reporting can help investors and other stakeholders assess a company's performance and risk profile, and inform decisions about investment, engagement, or advocacy. Increasingly, ESG reports and ratings is becoming a standard practice among companies, as stakeholders demand greater transparency and accountability on ESG issues.
What does ESG mean in business?
In the context of business, ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance. ESG financial has become an important framework for assessing a company's long-term sustainability and ethical practices, and it is increasingly being used by investors and other stakeholders to evaluate the overall impact of a company beyond its financial performance.
Environmental factors refer to a company's impact on the natural environment, such as its carbon footprint, energy consumption, waste management practices, and water usage. Companies that are committed to reducing their environmental impact are often seen as more sustainable and attractive to investors who prioritize sustainable practices.
Social factors refer to a company's impact on society, including its relationships with employees, customers, suppliers, and the communities where it operates. This includes factors such as diversity, equity, and inclusion, human rights, labor practices, and product safety. Companies that prioritize social responsibility and ethical behavior are often seen as more trustworthy and sustainable.
Governance factors refer to a company's internal governance structure, including its board of directors, executive compensation, shareholder rights, and transparency in financial reporting. Companies that prioritize good governance practices are often seen as more accountable and trustworthy, which can help attract investors and build long-term value.
Overall, ESG has become an important way to assess a company's overall impact on society and the environment, as well as its ability to create long-term value for its stakeholders.
How Do I Know Which Investments Are ESG?
Identifying ESG investments can be a challenge, as the term ESG can be used in different ways by different organizations and investment managers. However, there are a few approaches you can take to identify ESG investments:
- Look for ESG funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs): Many investment managers offer ESG funds or ETFs that screen companies for their ESG corporate governance performance. These funds are designed to help investors achieve their financial goals while investing in companies that meet certain ESG criteria. You can search for ESG funds or ETFs through financial websites or consult a financial advisor for recommendations.
- Use third-party ESG ratings: Various organizations provide ESG ratings or scores that assess the ESG performance of companies. These ratings can help you identify companies with strong ESG performance, which can guide your investment decisions. Examples of third-party ESG ratings providers include MSCI, Sustainalytics, and Morningstar.
- Conduct your own research: You can also research individual companies to assess their ESG performance. Many companies have ESG information available on their websites or in their annual reports. You can also look for news articles or other sources that provide information on a company's ESG practices and impact.
It's worth noting that different investors may have different views on what constitutes an ESG investment, so it's important to determine your own corporate ESG priorities and assess investments accordingly. Additionally, investing involves risks and potential loss of principal, so it's important to conduct your own due diligence and consult with a financial advisor before making any investment decisions.
Read more This Blog :- What is the ESG framework in India?



Comments
Post a Comment