What is ESG and Why is it Important?
ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance, and it refers to a set of criteria used to assess the sustainability and ethical impact of an investment or a company's operations. ESG environmental factors are used to evaluate a company's performance in three main areas:
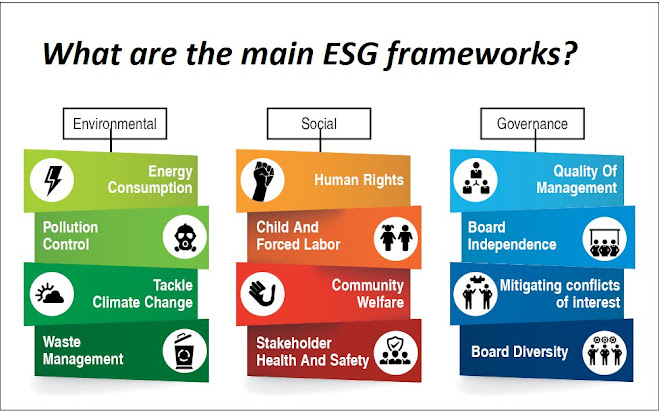
- Environmental: This refers to a company's impact on the natural environment, including its carbon emissions, waste management, water usage, pollution, and other ecological factors. It also includes a company's efforts to mitigate and adapt to environmental risks and opportunities such as climate change and resource scarcity.
- Social: This refers to a company's impact on people, both within and outside the organization. It includes factors such as labor practices, human rights, diversity and inclusion, community relations, customer satisfaction, and product safety. It also encompasses issues like employee well-being, health and safety, and supply chain management.
- Governance: This refers to the systems and processes by which a company is directed, controlled, and held accountable. It includes factors such as board composition, executive compensation, shareholder rights, transparency, risk management, and business ethics. Good governance ensures that a company is managed in a responsible and ethical manner, and that the interests of various stakeholders, including shareholders, employees, and customers, are considered.
ESG is important for several reasons:
- Risk management: Companies that effectively manage their ESG risks are better positioned to mitigate potential environmental, social, and governance-related risks that could impact their financial performance and reputation. For example, companies that are heavily reliant on fossil fuels may face financial risks due to increasing climate regulations and changing consumer preferences towards sustainable alternatives.
- Long-term sustainability: Companies that prioritize ESG factors are often better positioned for long-term sustainability and resilience. By addressing environmental and social issues, companies can contribute to the well-being of the communities they operate in, build strong relationships with stakeholders, and reduce reputational risks, which can lead to improved financial performance over the long term.
- Stakeholder expectations: Investors, consumers, employees, and other stakeholders are increasingly considering ESG factors in their decision-making. Investors are looking for companies that are socially responsible and aligned with their values, while consumers are demanding products and services that are environmentally and socially responsible. Employees are also seeking to work for companies that prioritize ESG, as it aligns with their personal values and sense of purpose.
- Regulation and compliance: ESG-related regulations and ESG reporting requirements are becoming more prevalent around the world. Companies may face legal and regulatory risks if they do not comply with ESG-related laws and regulations, which could result in financial penalties, reputational damage, and loss of business opportunities.
- Innovation and opportunities: Embracing ESG can also drive innovation and create new business opportunities. Companies that develop environmentally friendly technologies or socially responsible products and services can tap into growing markets and gain a competitive advantage. ESG considerations can also help companies identify and manage emerging risks and opportunities, which can lead to improved operational efficiencies and cost savings.
In summary, ESG is important because it helps companies manage risks, promotes long-term sustainability, meets stakeholder expectations, ensures compliance with regulations, and creates business opportunities. It has become a critical factor in investment decision-making and corporate governance, and companies that proactively integrate ESG considerations into their strategies are likely to be better positioned for success in the evolving business landscape.
Explainer what is ESG and why is it important
ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance, and it refers to a set of criteria used to assess the sustainability and ethical impact of an investment or a company's operations. ESG factors are used to evaluate how well a company performs in three main areas:
- Environmental: This refers to a company's impact on the natural environment, such as its carbon emissions, waste management, water usage, and pollution. It also includes a company's efforts to address environmental risks like climate change and resource depletion.
- Social: This refers to a company's impact on people, both within and outside the organization. It includes factors such as labor practices, human rights, diversity and inclusion, community relations, customer satisfaction, and product safety. It also encompasses issues like employee well-being, health and safety, and supply chain management.
- Governance: This refers to the systems and processes by which a company is directed, controlled, and held accountable. It includes factors such as board composition, executive compensation, shareholder rights, transparency, risk management, and business ethics. Good governance ensures that a company is managed responsibly and ethically, and that the interests of various stakeholders are considered.
ESG is important for several reasons:
- Risk management: Companies that effectively manage their ESG risks are better positioned to mitigate potential environmental, social, and governance-related risks that could impact their financial performance and reputation. For example, companies that are heavily reliant on fossil fuels may face financial risks due to increasing climate regulations and changing consumer preferences towards sustainability consulting alternatives.
- Sustainability: Companies that prioritize ESG factors are often better positioned for long-term sustainability and resilience. By addressing environmental and social issues, companies can contribute to the well-being of the communities they operate in, build strong relationships with stakeholders, and reduce reputational risks, which can lead to improved financial performance over the long term.
- Stakeholder expectations: Investors, consumers, employees, and other stakeholders are increasingly considering ESG factors in their decision-making. Investors are looking for companies that are socially responsible and aligned with their values, while consumers are demanding products and services that are environmentally and socially responsible. Employees are also seeking to work for companies that prioritize ESG, as it aligns with their personal values and sense of purpose.
- Regulation and compliance: ESG-related regulations and reporting requirements are becoming more prevalent around the world. Companies may face legal and regulatory risks if they do not comply with ESG-related laws and regulations, which could result in financial penalties, reputational damage, and loss of business opportunities.
- Innovation and opportunities: Embracing ESG can also drive innovation and create new business opportunities. Companies that develop environmentally friendly technologies or socially responsible products and services can tap into growing markets and gain a competitive advantage. ESG considerations can also help companies identify and manage emerging risks and opportunities, which can lead to improved operational efficiencies and cost savings.
In summary, ESG is important because it helps companies manage risks, promotes long-term sustainability, meets stakeholder expectations, ensures compliance with regulations, and creates business opportunities. It has become a critical factor in investment decision-making and corporate governance, and companies that proactively integrate ESG considerations into their strategies are likely to be better positioned for success in the evolving business landscape.
What is the purpose of ESG?
The purpose of ESG is multifaceted and can vary depending on the stakeholders involved. Some of the key purposes of ESG include:
- Assessing sustainability: ESG is used as a framework to assess the sustainability and ethical impact of an investment or a company's operations. It helps evaluate how well a company is managing its environmental, social, and governance risks and opportunities, and whether it is operating in a sustainable and responsible manner.
- Managing risks: ESG enables companies to identify, assess, and manage various risks related to environmental, social, and governance factors. For example, it helps companies identify and mitigate risks associated with climate change, resource depletion, labor practices, human rights violations, and reputational risks. By addressing these risks, companies can reduce potential negative impacts on their financial performance, reputation, and stakeholder relationships.
- Promoting sustainability: ESG encourages companies to adopt sustainable business practices that consider the long-term impacts on the environment, society, and governance. It promotes responsible resource management, environmental conservation, social inclusiveness, and ethical business conduct. By prioritizing sustainability, companies can contribute to the well-being of communities, protect the environment, and support social progress.
- Meeting stakeholder expectations: ESG helps companies align with the expectations of various stakeholders, including investors, consumers, employees, regulators, and communities. Investors are increasingly looking for companies that demonstrate responsible and sustainable business practices, while consumers are demanding products and services that are environmentally and socially responsible. Employees are also seeking to work for companies that prioritize ESG, as it aligns with their personal values and sense of purpose. By meeting stakeholder expectations, companies can build trust, loyalty, and goodwill among their stakeholders.
- Enhancing corporate governance: ESG emphasizes the importance of strong governance practices within companies. It promotes transparency, accountability, and ethical behavior in decision-making and operations. By enhancing corporate governance, companies can build trust with investors, ensure compliance with regulations, and reduce the risk of fraud, corruption, and other unethical practices.
- Driving innovation and business opportunities: ESG can foster innovation by encouraging companies to develop environmentally friendly technologies, socially responsible products and services, and sustainable business models. It can also create new business opportunities in emerging markets, as there is increasing demand for sustainable solutions. By driving innovation and seizing business opportunities, companies can gain a competitive advantage and create value for their stakeholders.
Overall, the purpose of ESG is to promote responsible and sustainable business practices that consider the environmental, social, and governance impacts of a company's operations, and to align with stakeholder expectations for long-term sustainability, resilience, and value creation.
What are the documents required for ESG certification?
ESG certification typically involves a thorough assessment of a company's environmental, social, and governance practices, policies, and performance. The specific documents required for ESG certification may vary depending on the certifying organization or standard being followed. However, some common documents that may be required for ESG certification include:
- Environmental Documents: These may include environmental policies, environmental management system (EMS) documentation, environmental impact assessments (EIAs), greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions data, waste management plans, energy management plans, and reports on environmental performance indicators.
- Social Documents: These may include social policies, human rights policies, labor practices and employee relations documentation, community engagement plans, diversity and inclusion policies, health and safety management plans, social impact assessments, and reports on social performance indicators.
- Governance Documents: These may include corporate governance policies, board charters, codes of conduct, anti-corruption policies, risk management plans, internal control documentation, shareholder engagement plans, executive compensation policies, and reports on governance performance indicators.
- Financial Documents: These may include financial reports, audited financial statements, annual reports, and any other relevant financial documents that demonstrate the financial stability and performance of the company.
- Sustainability Reports: These may include comprehensive reports that provide detailed information on the company's ESG practices, policies, goals, and performance. Sustainability reports typically cover a wide range of topics related to ESG, and may be prepared in accordance with recognized reporting frameworks such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), or the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD).
- Other Relevant Documents: Depending on the specific ESG certification requirements, additional documents may be required, such as certifications, licenses, permits, relevant legal and regulatory documents, and any other documentation that supports the company's ESG claims.
It's important to note that the specific documents required for ESG reporting in India certification may vary depending on the certifying organization or standard being followed. It's recommended to carefully review the certification requirements and guidelines provided by the certifying organization or standard to ensure that all necessary documents are prepared and submitted accurately.
Read more This Blog :- How ESG Strategies Can Help Companies Mitigate Risk and Enhance Resilience.



Comments
Post a Comment